This paper addresses issues within the realm of legal work by employing event extraction technology on the case description section of Chinese legal texts, specifically focusing on larceny cases. The authors define event types, event arguments, and their roles in larceny cases. They create a dataset for event extraction through data annotation and divide the extraction process into two stages: identifying event trigger words and jointly extracting arguments, followed by assigning event argument roles. The methodology involves utilizing BERT for Chinese character vectors, employing a BiLSTM-CRF model for initial extraction, integrating additional features, and using a CRF model for improved extraction. The extracted event data is presented in a chronological sequence to facilitate litigation visualization. The paper also discusses formatting Chinese time expressions, sorting event information chronologically, and introducing a web application for displaying the event timeline. The primary focus areas are Chinese legal text, event dataset creation, event extraction, and litigation visualization.
Introduction
- Formalize the legal event extraction problem and present the required extraction pipeline
- Demonstrate the utility of the proposed extraction method
- Utilize Joint Extraction on multi-source elements and improve the performance of event extraction from legal text
Related Work
- Event Extraction
- Event Graph Construction
- Legal Intelligence Research
Related research for this paper included Event Extraction, Event Graph Construction, and Legal Intelligence Research, We reviewed relevant studies that applied event extraction techniques across a variety of domains, including news articles, biomedical literature, and social media. It highlighted the specific challenges faced when applying event extraction techniques to legal texts due to the complexity and ambiguity of legal language and the importance of event extraction in the legal domain to help legal professionals evaluate and judge cases.
Approach
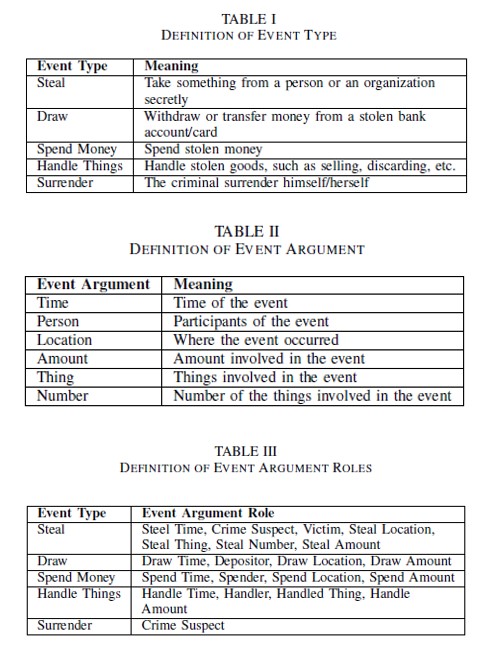
- Definition of Event Elements
- Targeting theft cases
- Define the five frequent events in a theft case
- Define event types, event arguments, and the role of event arguments
- Data Processing
- Chinese AI and Law (CAIL) 2018, Criminal case texts from news, websites, etc.
- Selected 3,000 texts from raw data
- Removed sentences that did not contain predefined events to eliminate noisy samples
- Obtained 6,538 sentences containing predefined events
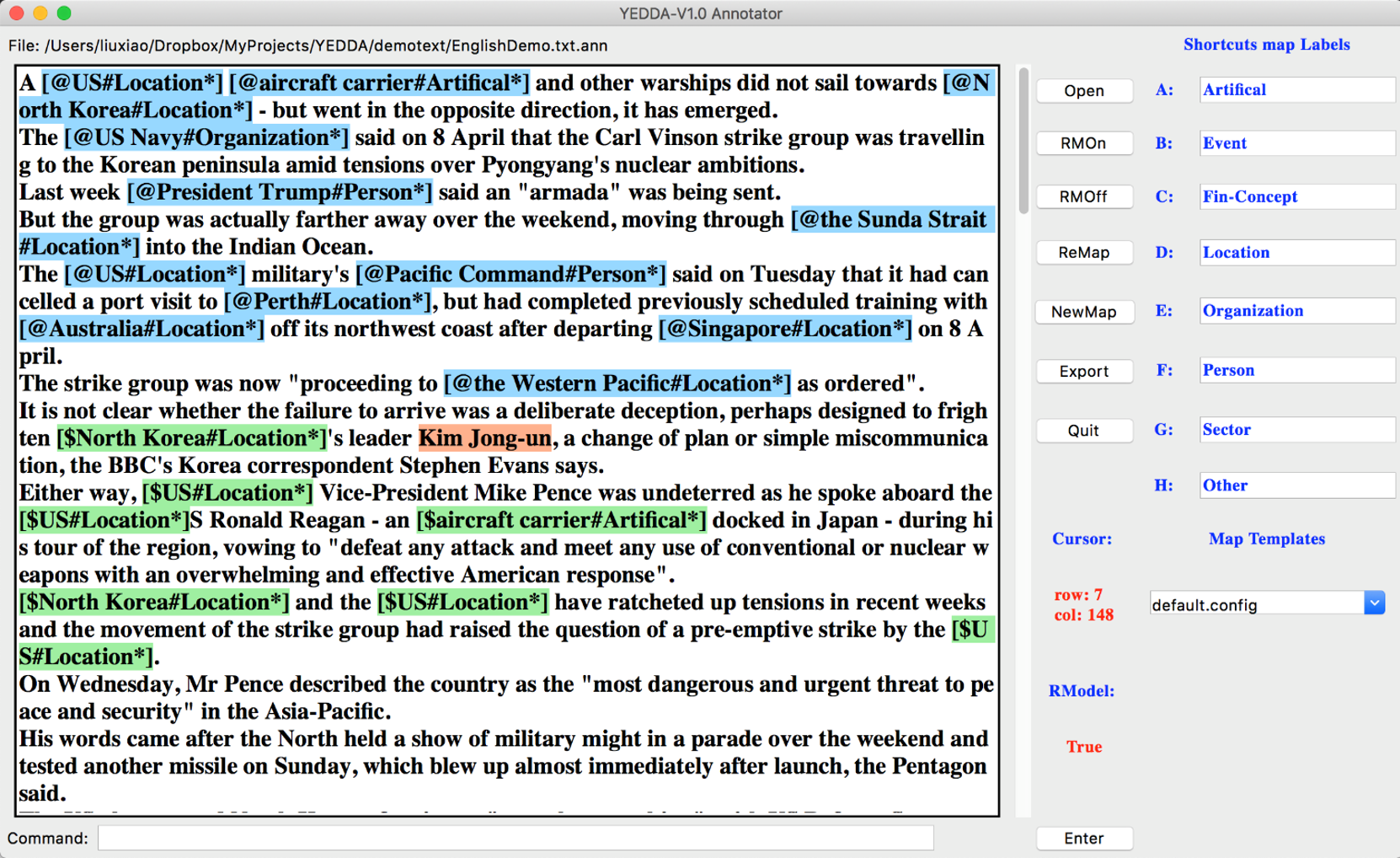
Data labeling tool: YEDDA Labeling scheme: BIO scheme
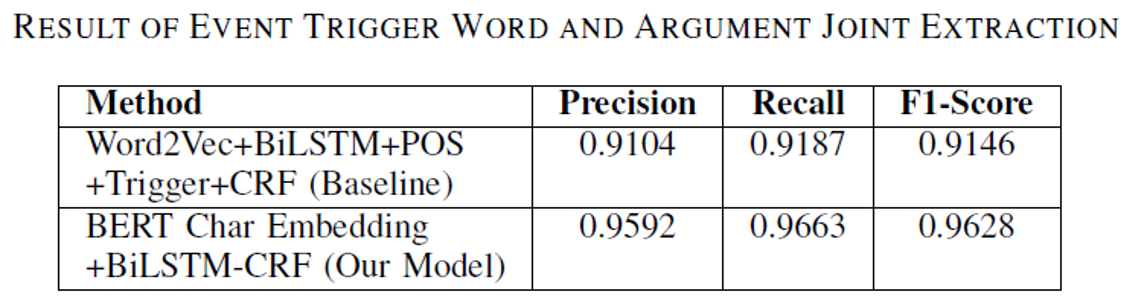
- Event Extraction
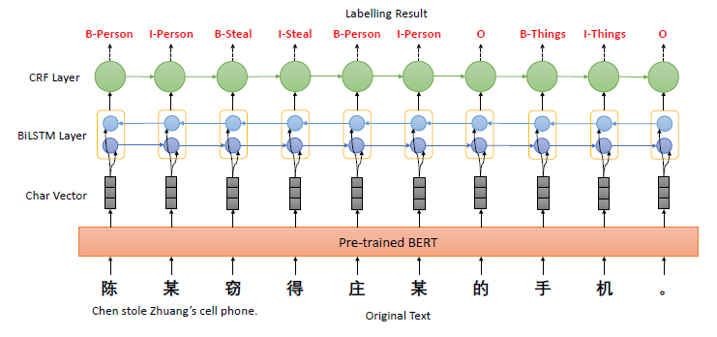
- Pre-trained BERT embeds text to obtain character vectors. → Input to BiLSTM-CRF model to obtain extraction results.
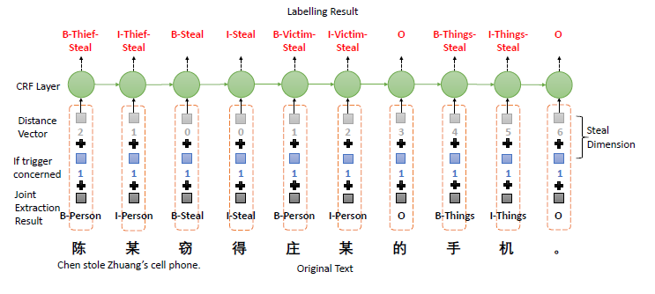
- Combine 3 vectors (argument extraction result, related trigger vector, and distance vector) and input to CRF model to extract argument’s role
Experiments
- Baseline
- Using precision, recall, and F1-score as evaluation metrics
- Baseline model: 2 steps
-
Step 1: Generate word vectors with word2vec Extract semantic information with BiLSTM and combine it with part-of-speech tagging results and IsTrigger vectors Extract transition labels using a CRF model
-
Step 2: Use CRF model to extract trigger types and argument types and roles
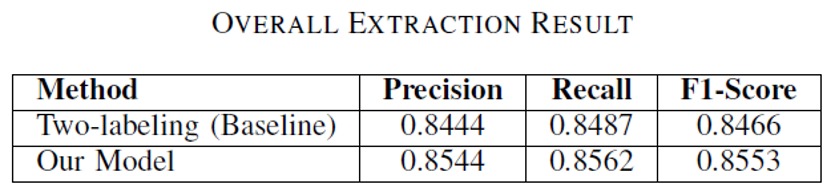
-
- Experiment Results
- training: 10-fold cross-validation method (1 randomized validation set, 9 training sets)
- Update weights using Adam Optimizer
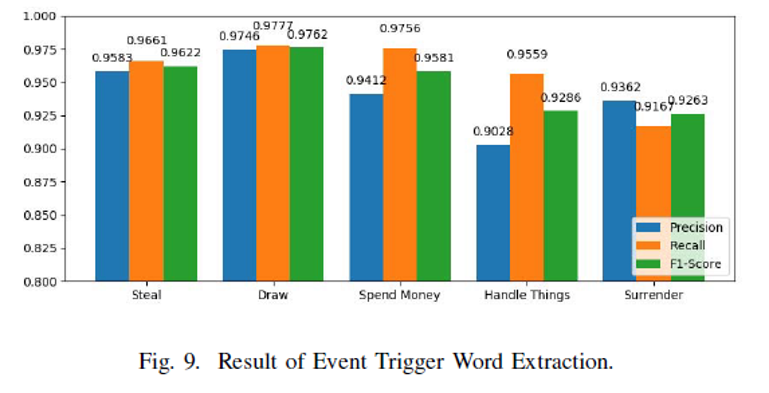
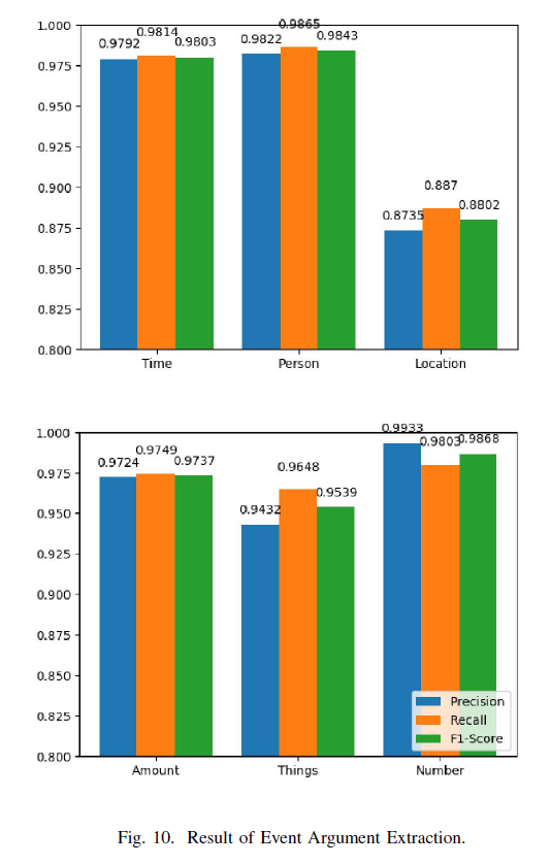
Event argument extraction results are generally good. The reason for the relatively poor extraction results for location entities is that they have a more irregular representation.
Conclusion
- Visualized the extracted event information.
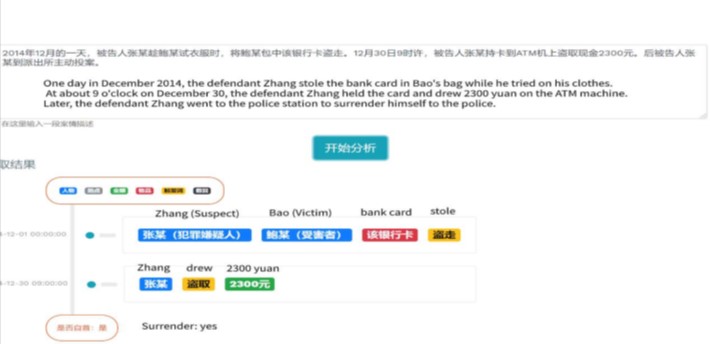
- There are some work needs to be done in the future: In terms of the allocation of event elements, this research does not deal well with the case where there are multiple events in the same sentence and the event elements are distributed across sentences.
- Future work includes breaking the limitations of event templates and applying event extraction techniques to various types of cases.



